Geometry can be considered the fun part of mathematics due to the drawings we have to make based on calculus. It’s quite fascinating to see how a certain number indicates an angle or where multiple lines meet and become a shape.
The basic shapes in mathematics are taught in middle school even though students should be able to recognize them already from games that enhance visual memory.
Let’s make sure you memorize the fundamental geometrical shapes so you can, later on, solve complex geometry problems.
The 5 most common geometric shapes
These shapes have built up the world. You can see them on the street, in the architecture of buildings, in the structure of your furniture or your jewelry. The world has been built on: circles, squares, rectangles, and triangles.
The Circle

A circle is a geometrical shape that we can create by drawing a curved line from one end to another, respecting the same distance around a specific point (center of the circle).
When we calculate the dimensions of a circle, we refer to its: circumference, center, radius, chord, and diameter.
Circumference: The circumference of a circle refers to the numerical value of the outer line of the circle.
How do we calculate the circumference?
In order to determine the circumference of a circle, we need to know its diameter or radius. Thus, we have the following formulas:
C = 𝝿 d, where C is the circumference, 𝝿 is 3.14159 and d is the diameter.
Or,
C = 2𝝿 r, where C is the circumference, 𝝿 is 3.14159 and r is the radius.
Chord: The chord of a circle refers to any segment or line drawn from one point of the circle to another point of the circle. The diameter of the circle would be the longest chord.
The length of the chord is calculated with this formula: 2 x (r2– d2)
Center
The center of a circle is the point from which all the points on the circle are at the same distance.
How can we find the center of a circle?
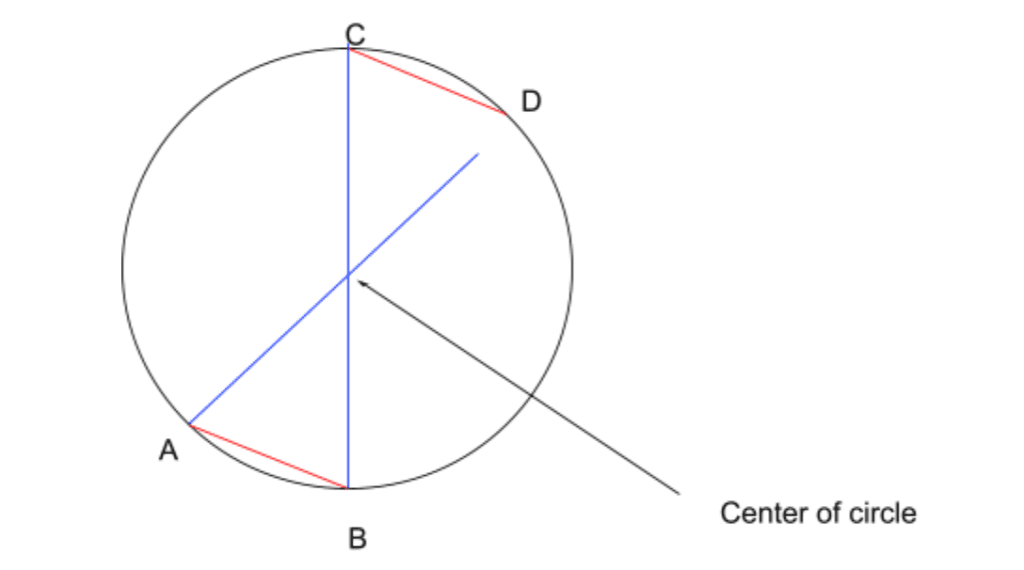
In order to find the center of a circle, we need to draw a chord. Name the first chord AB for keeping track easily. Draw a second chord, parallel and of the same length as AB, and name it CD. Unite the points in a cross: A to D, and B to C.
The intersection point should be the center of the circle.
Diameter: is the chord that passes through the center of the circle, thus making it the longest chord.
The diameter of a circle is 2 x the radius of a circle.
Diameter’s formula: D = 2r.
D = C𝝿, where C is the circumference of the circle and 𝝿 (pi) is 3.14159.
Or, in case we know the area of a circle, we use the formula:
D = 2A𝝿 , where A is the area divided by 𝝿 (pi) = 3.14159
The radius is a segment or a line drawn from the center of a circle to any point on the circle.
When we know the circumference of the circle, we can calculate the radius with the next formula: r = C2𝝿
If we know the area of the circle, we use the following formula: r = A𝝿
Or, if we know the diameter, we simply divide the diameter by 2.
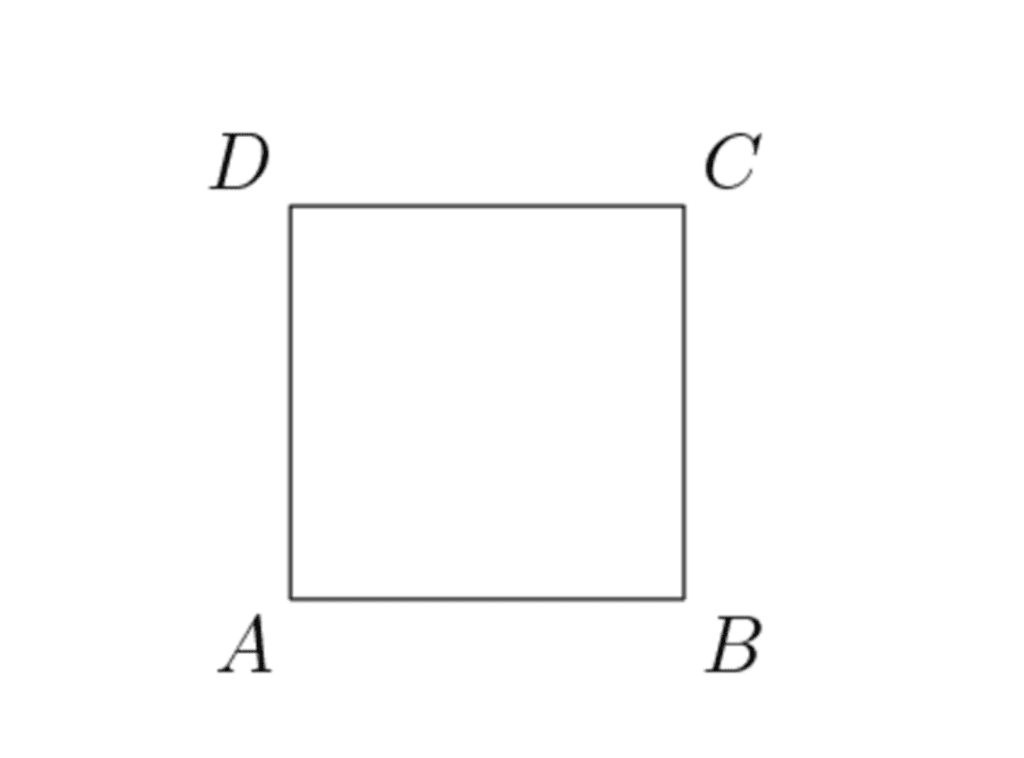
The Square
A square is a geometrical shape formed of 4 parallel and equal lines. The 4 lines form 4 equal right angles of 90° each.
The square has three elements: area, diagonal, and perimeter.
The Area is the total of the side lengths of a square.
We can determine the area of a square, by using this simple formula: Area (A) = a2 = a × a
The perimeter of a square is the outer length around the square, just like the circumference of a circle.
We can calculate the perimeter of a square by this formula: P = 4a, a being the sideline of the square.
The diagonal of a square is the line that cuts the square into two equal triangles from one corner to another. A square has two equal diagonals, which intersect in the middle.
The formula for the diagonal is d = a × 2 , where a is the sideline of a square.
The Rectangle
A geometrical shape with 4 lines of 2 different and equal dimensions. The opposite sides are parallel and of equal length.
Similar to the square, we can calculate the area, perimeter and diagonals of a rectangle.
The formula of the area of a rectangle is: a x b, where a is one of the longest side lines and b is one of the shortest side lines.

Formula for a rectangle’s perimeter: 2 (a+b).
Formula for a rectangle’s diagonal: (a2+ b2), a rectangle has two diagonals of identical lengths which intersect in the middle.
The Triangle
A triangle is a geometric figure composed of three side lines and three angles.
There are 3 types of triangles: equilateral, isosceles and scalene. Each of these types comes with some particularities. We can also differentiate triangles according to their specific angles, there are:
- Acute triangles with ALL angles < 90°.
- Right triangles with ONE right angle = 90°.
- Obtuse triangle with ONE angle > 90°.
Measuring triangles and calculating laterals and angles of triangles has been a great part of geometry.
Pythagora even came up with a special theorem about triangles, therefore, the OMC math tutors will dedicate a whole article to triangles for math-lovers, so stay close to us.
Follow our blog for more useful and fun information on mathematics.
Ready to learn more math? Our OMC math tutors offer individual and group math lessons to middle school students.
Contact us for a tailored math tutoring plan, anytime!