Mathematics is not solely about clear numbers and simple calculations. Mathematics also deals with relations between numbers, variables, and fractions. This might get a bit more complicated, but keep following our Math Symbols and Their Meanings series as we set out to unwrap the beautiful language of mathematics.
What is Set Theory?
Set Theory is a branch of mathematics that concerns collections or sets of numbers and fractions. But, first, let’s break it down. The theory is a set of rules by which elements behave or relate to each other.
A set is an unordered collection of objects, elements, fractions, or variables. An element that belongs to a set is indicated with the following symbol: a ∈ A (element a belongs to set A), a ∉ A (element a does NOT belong to set A).
Sets can be represented through 3 methods:
- Statement form
- Roaster form or tabular form method
- Set Builder method
In the statement form, elements of the set are described in a clear way. Check the examples below:
- A set of odd numbers between 3 and 17.
- A set of students in 4th grade with heights equal or smaller than yours.
In the roaster form, also referred to as the tabular form, elements are listed inside pairs of brackets, separated by commas, such as:
- M is the set of even numbers less than 14
M= { 2 , 4 , 6, 8, 10, 12 }
- F is the set of all weekdays.
F = { Monday, Tuesday, … , Sunday }
In the builder form, the set is defined by a property all its members have to satisfy. Look at the examples below:
- G = {x : x is a counting number and lesser than 24}
- N = {x | x, is an even natural number less than 15}
Now that we have explained the three ways in which a set can be represented, let’s continue with the types and sizes of sets.
Types Of Sets
- Equal sets – two sets are equal if they have the same elements, not necessarily the same order of elements. Example: F = { 3, 5, 7, 9 } and U = { 5, 9, 7, 3 } are equal sets.
- Subsets – when a set is a subset of another set, it means that any element of the subset is also an element of the main set. Subsets are indicated by the symbol “⊆”.
Example: “A ⊆ B” denotes A is a subset of B.
In math exercises, you can encounter situations in which you are required to show that if x belongs to set A, then x also belongs to set B, since A is a subset of B.
Size Of Sets
A set can be either finite or infinite. The size of the set is given by the conditions the members of the set have to satisfy. For example, a finite set has the following condition: natural numbers less than 80, thus we know that the finish of the set is 79.
An infinite set of numbers has a general condition, such as the set of real numbers, or the set of odd numbers.
The size of a set is called a cardinality number and it is indicated with the following symbol “|letter of set|”, as you can see in the example below:
- F is a set of odd numbers less than 11
Solution: F = {1,3,5,7,9}. The cardinality of the set is 5 (there are 5 elements in the set), therefore |F| = 5.
Please remember the fact that the cardinality or size of a set is determined by the number of members in that particular set. A null set has the cardinality number 0.
A Special Treat – Power Sets And Cartesian Products
We also want to mention the “power sets” before we dive into the set operations. Power sets indicate all the possible subsets of a given set. It is indicated with the following symbol P(letter of set).
For more clarity, check the example below:
What is the power set of {0,1,2}?
Solution: All possible subsets of set {0,1,2} are: {∅}, {0}, {1}, {2}, {0,1}, {0,2}, {1,2}, {0,1,2}.
Did you know that power sets also have cardinality?
The cardinality of a power set is equal to the number of elements in a set.
Try to solve this example on your own and then check the solution:
The cardinality of the power set of {0, 1, 2 . . ., 10} is _________.
(A) 1024
(B) 1023
(C) 2048
(D) 2043
Do you know what a cartesian product is in a set?
A Cartesian product is a set of all ordered pairs where one element belongs to a set and another element belongs to another set. Cartesian product is indicated with the multiplication symbol, such as: M x N.
For example, we have two sets, M and N.
What is the Cartesian product of M = {1,2} and N = {a, b, c}?
Answer: M x N = {(1, a), (1, b), (1, c), (2, a), (2, b), (2, c) };
Exercise: Let A={John, Jim, Dave} and B={Mary, Lucy} be two sets. Determine A x B and B x A. (Note that when it comes to cartesian products: A x B ≠ B x A). Try to solve the exercise by yourself and then check the solution.
Are You Ready For Set Operations Now?
SET OPERATIONS
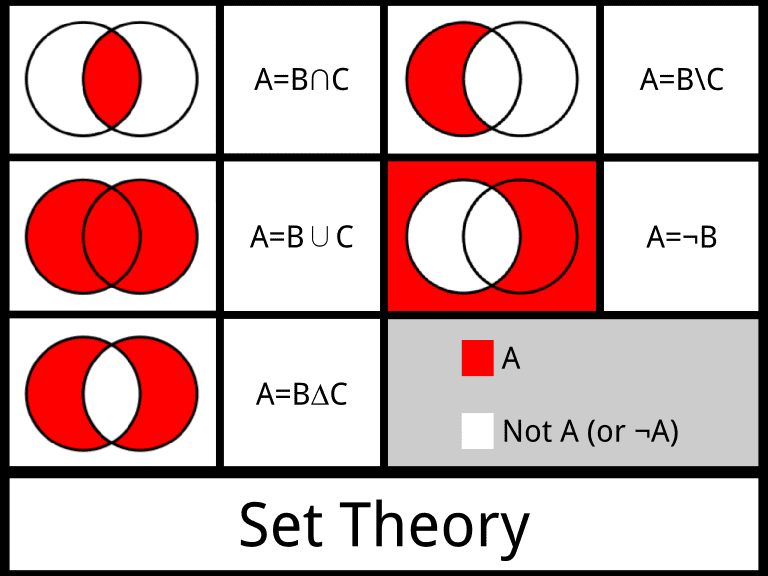
In order to represent different set operations, in mathematics, we use the Venn Diagram. The Venn Diagram was invented in 1880 by British logician John Venn in order to describe the relations between sets, in a logical manner. It started to be used in the math curriculum around the 1960s and since then, mathematicians use it as a basic tool to represent operations of sets.
There are 6 main set operations:
Union – indicated by the symbol “∪”, it denotes the distinct elements that belong to A, B or both.
Example: What is the union of A = {7, 8, 9} and B = {5, 6, 7}?
Answer: A ∪ B = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
Intersection- indicated by the symbol “∩”, it refers to the common elements that belong to set A and set B.
Example: What is the intersection of A = {0,7, 8, 9} and B = {0, 5, 6, 7}
Answer: A ∩ B = {0, 7}
Disjoint – it is shown by graphical shapes and it indicates the fact that there is no commonality between set A and set B. They are two distinct sets.
Difference – it is indicated by the minus symbol “-” and it shows the elements that can be found in set A, but not in set B.
Example: What is the difference between A = {7, 8, 9} and B = {5, 6, 7}?
Answer: A – B = {8,9}
Complement – indicated by the symbol “setc”, it shows all the elements except those in the named set.
Example: Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and A = {1,3}. Find Ac
Answer: Ac = U-A = {2, 4, 5}
Addition And Subtraction
The addition is also known as Minkowski addition and can be possible only for numeric elements. The added set contains the elements which are the sum of each possible pair of elements from set A and set B.
Example: What is the addition between sets A = {7, 8, 9} and B = {5, 6, 7}?
Answer: A + B = {(7+5), (7+6),(7+7), (8+5), (8+6), (8+7), (9+5), (9+6), (9+7)}
Subtraction is the opposite operation of the addition, it can also be used only numerically. It can be indicated by “-” , or “\” symbols. It shows the number that belongs to another set, the difference between the two sets.
Example: What is the subtraction of the two sets A = {7, 8, 9} and B = {5, 6, 7}?
Answer: A\B = {8,9} , while B\A = {5,6}
Since you are already getting the hang of set operations, you can enjoy some of the exercises available online.
Don’t Forget That…
We are always available to tutor middle to high school students who are ready to tackle the challenges of math in an efficient and fun way.
Online Math Center offers a suite of tutoring programs including individual tutoring.
Reach out to us for any kind of information regarding our math tutoring opportunities.